24
Introduction
Area of Gandhinagar Capital Project was a part
of villages which lacked development in terms of
agriculture and basic amenities before selection
of the site for capital of a new state-Gujarat.
After bi-furcation of Bombay state in 1961, the
Gujarat Government started functioning from
Ahmedabad. Subsequently, the Government
identified the area near Ahmedabad along
Sabarmati River to be named as Gandhinagar
as the Capital of Gujarat. A master plan of
Gandhinagar was designed and finalised after
identification of area in 1966. Before this, the
major part of Gandhinagar was a part of dusty
ravines of Sabarmati. Tree cover was very poor,
although there is no report which provides
information about the status of vegetation in the
area. At present, the area of Candhinagar Capital
Project is 5,700 ha and it has been divided in 30
sectors
,
and large areas, mostly along both sites
of Sabarmati River, were demarcated separately
and were excluded from development in the
initial stage. Now development of institutions
and offices has started in those areas also.
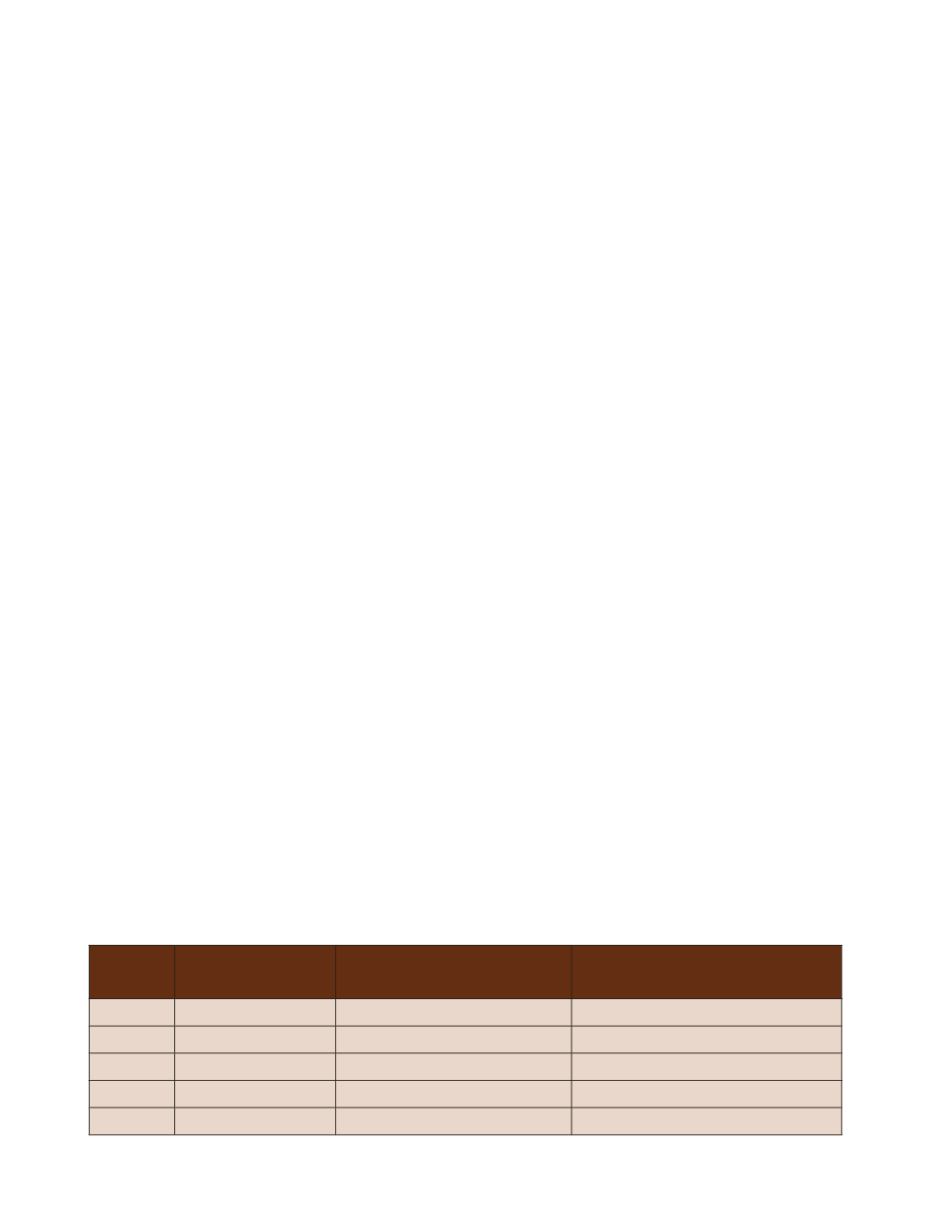
Table-9 : Plantations during the last four decades in Gandhinagar Capital Project Area
Year
Area of plantation
(area in ha)
No of seedlings planted by
the Forest Department
Average annual rate of
plantation(seedlings/year)
1971-80
535.1
1,071,000
107,000
1981-90
328.1
382,500
38,250
1991-00
1063.9
1,665,900
166,600
2001-10
562.5
351,310
35,130
Total
2489.6
3,470,710
86,750
13. Status of tree cover in different Municipal Corporations
13.1 Trees in Gandhinagar Capital Project Area
(Gandhinagar Municipal Corporation Area)
Plantation in Capital Project Area
Capital development works were started in
1967 and the Forest Department was entrusted
the work to afforest ravines and other areas
to provide a background of the green city.
Subsequently, Gandhinagar Forest Division was
constituted in 1973. The tree plantations were
taken up in ravines, along roads and railways,
campus areas of the Government buildings,
educational institutions and industrial areas.
Some areas were marked for development of
offices, buildings, and institutions in future. In
the absence of plan at that time, these areas
were also planted in 1990s to maintain block
plantations till the period of their development.
The details of plantations by the department
during the last four decades are given in Table-9.
A good number of labourers camp in the city
area and they extract fuel wood from the dead
branches or dead trees. Every year, a good
number of trees dry and small dead trees of
them were gradually used by the people for
firewood. Such trees are not accounted and
reflected in the figure of officially removed
trees. Thus
,
official data of dead and fallen trees
and also illegally cut trees do not present true
picture.


