10
4. Tree Cover in Urban Areas in India
The Delhi-based National Institute of
Environment Studies (NIES) prepared a list of
major cities with tree cover and mentioned that
Calcutta has the lowest green cover (less than
one per cent of geographical area) among all
mega cities
23
. The NIES estimated a tree cover
of 8.60 per cent in Bangalore; 11.9 per cent in
New Delhi; 6.20 per cent in Greater Mumbai;
and 7.5 per cent in Chennai. According to
the norms, mentioned by the NIES and some
other literature, the tree cover should be at
least 15 per cent for megacities with a million-
plus population
23
. Thus, majority of the cities,
including the green cities, in India have tree
cover below the minimum optimum norm.
Due to lack of space and demand of the land
for other purpose, it may be difficult to achieve
the tree cover of 15% of city area or 20 m
2
per
inhabitants in the megacities like Ahmedabad
and Surat. In such cities, the goal of achieving
tree cover of 10 % of the geographical area or
10-15 m
2
tree cover per inhabitant may be a
realistic target.
Like the ChineseGovernment, Delhi Government
has done commendable job to expand forest and
park garden before the Common Wealth Games
2010. At present 20%of Delhi’s geographical area
is under green cover (11.9%under tree cover and
the rest under garden and parks with grasses),
making per capita green space availability to
around 21.43 m
2
. Municipal Corporation of Delhi
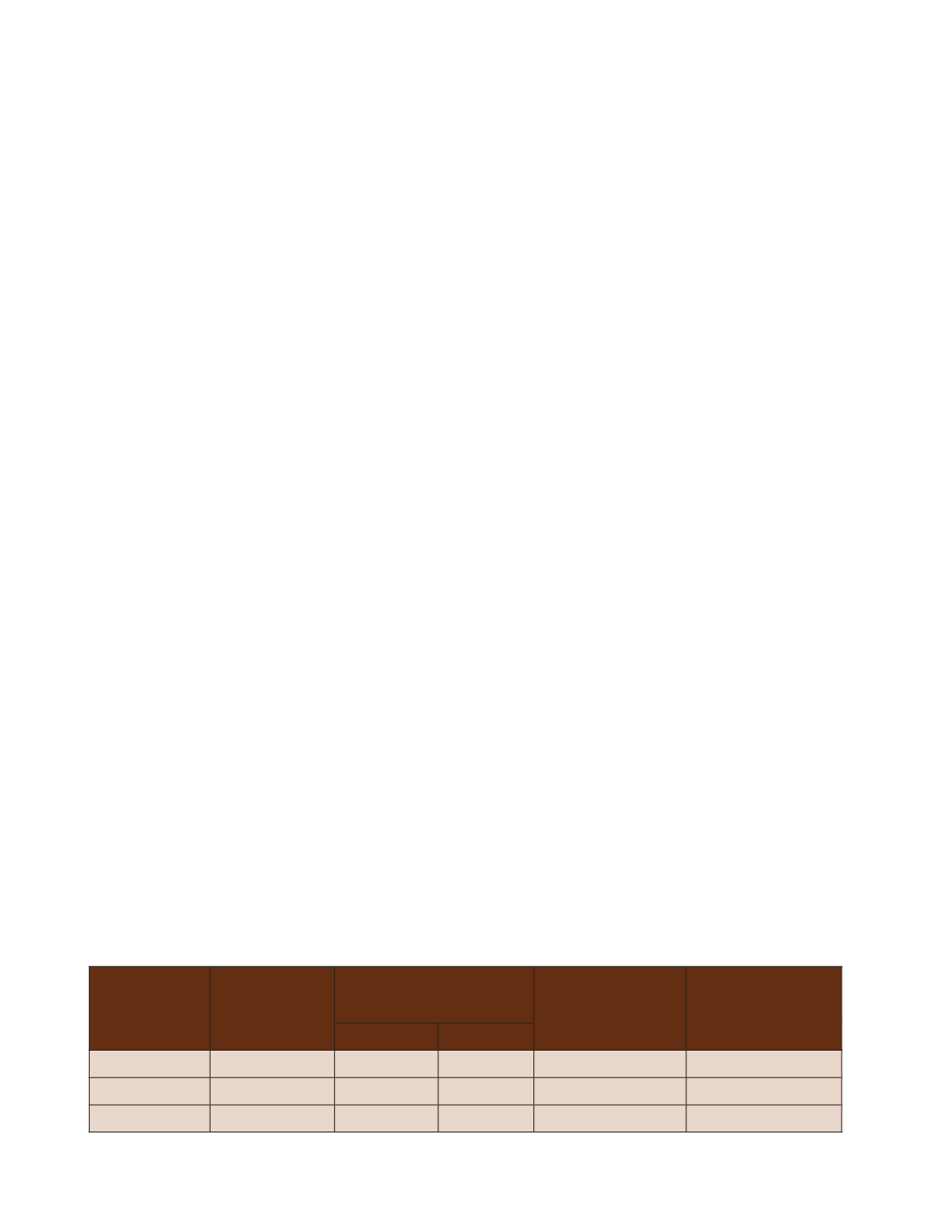
Table-1: Tree and forest cover in the urban areas of Delhi, Chandigadh and Gandhinagar
Name of city
Total
geographical
area (sq. km.)
Forest and tree cover
(sq. km.)
Total tree and
forest cover (sq.
km)
Percent of
geographical area
Dense
open
Delhi
1,483
56
120
177
11.9%
Chandigadh
114
11
6
17
14.9%
Gandhinagar
57
21
10
31
53.9%
(MCD), New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC)
and Delhi Development Authority (DDA) have
many parks, city forests, biodiversity parks and
other green belts. There are nine city forests and
two biodiversity parks in Delhi. Nine more city
forests are planned to be created. Still there is a
need to identify vacant areas which can be put
under the green cover. Entire ridge area (about
6,000 ha) needs to be greened.
The status about the tree cover for different
cities in India is not available, but the Forest
Survey of India (2011)
20
reported forest and
tree cover in the two Urban Areas (Chandigadh
and Delhi) of the Union Territories. The Gujarat
Forest Department conducted a separate study
(2011)
21
to assess tree cover in Gandhinagar
Town Planning Area, and the comparable figures
have been given in Table-1.
InGujarat, about 26.9 crore trees (TOF) have tree
cover of 7837 sq. km., i. e 343 trees equivalent
to one hectare of tree cover. A study based on
remote sensing data has estimated tree cover
over an area of 3,075 ha in Gandhinagar which
is equivalent to 8.67 lakh trees (both estimates
are of the year 2011). Thus, about 282 trees,
distributed in the different girth classes above
10 cm, may be equivalent to one hectare of tree
cover in Gujarat. Since trees having lower girth
classes are relatively less and majority belong
to medium and large size trees, this equation
appears logical. The calculations regarding
tree cover in the cities presented in this report
are based on this equation. Sacramento’s
urban forest USA) has 13% tree cover which is
equivalent to 73 trees/ha
26
.
Source : FSI, Dehradun (2011)


